|
Lamprotornis australis (Burchell's
Starling)
Grootglansspreeu [Afrikaans]; Ndjundju
(generic term for starling) [Kwangali]; Kwezu leri kulu [Tsonga]; LegŰdilÍ
[Tswana]; Grote glansspreeuw [Dutch]; Choucador de Burchell [French];
Riesenglanzstar, Glanzelstar [German]; Estorninho de Burchell [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sturnidae > Genus: Lamprotornis
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from southern Angola and western Zambia to southern
Africa, where it is locally common in Namibia, Botswana and northern South
Africa. It generally prefers open woodland and savanna, especially with Camel
thorn (Acacia
erioloba) and Knob thorn (Acacia nigrescens) trees.
|
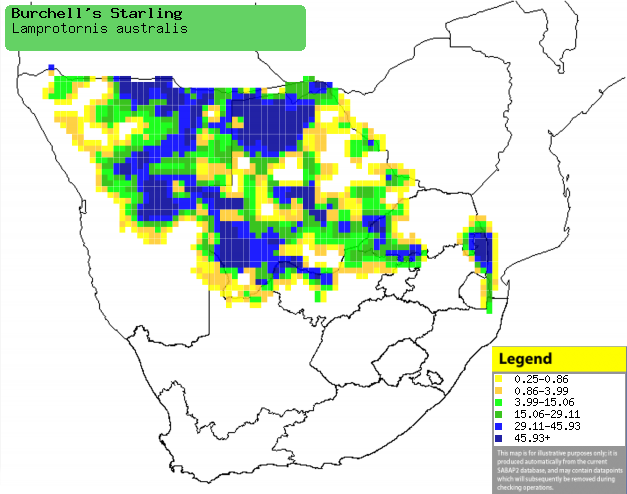 |
|
Distribution of Burchell's starling in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of
Aquila wahlbergi (Wahlberg's
eagle).
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Great spotted cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats arthropods, supplemented with small
vertebrates and fruit, doing most of its foraging on the ground. The following
food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Animals
- arthropods
- small vertebrates
- Plants
- fruit and flowers of Acacia trees
Breeding
- The nest (see image below) is usually a tree cavity, either natural or an
abandoned woodpecker or
barbet nest. It may also use a crevice
in a cliff, hole in a building or a nest box, lining the egg chamber with
grass, green leaves and feathers and sometimes cloth, paper, string and
snake skin.
 |
|
|
Burchell's starling at its nest hollow, Sericea
farm, South Africa. [photo
Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from October-April.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about 14
days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 20-24
days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts - Birds of
southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book
Fund, Cape Town.
|
