|
Eremomela icteropygialis
(Yellow-bellied eremomela)
Geelpensbossanger [Afrikaans]; Niini (generic term for
warblers and eremomelas) [Kwangali]; Timba (generic name for cisticolas
and warblers) [Shona]; Geelbuik-eremomela [Dutch]; Érémomèle à
croupion jaune [French]; Gelbbauch-eremomela [German];
Eremomela-de-barriga-amarela [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Sylviidae
> Genus: Eromomela
 |
 |
| Yellow-bellied eremomela, Vrolijkheid
Nature Reserve, Robertson, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Yellow-bellied eremomela, Uis, Namibia. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
It has two main populations in Africa; one stretches across
the Sahel from Mauritania to Sudan. The other occurs from Ethiopia
through Tanzania and Zambia to southern Africa. Here it is fairly common in the shrublands of the Kalahari and the Karoo, also occupying savanna woodland
(especially Acacia) and gardens.
|
 |
|
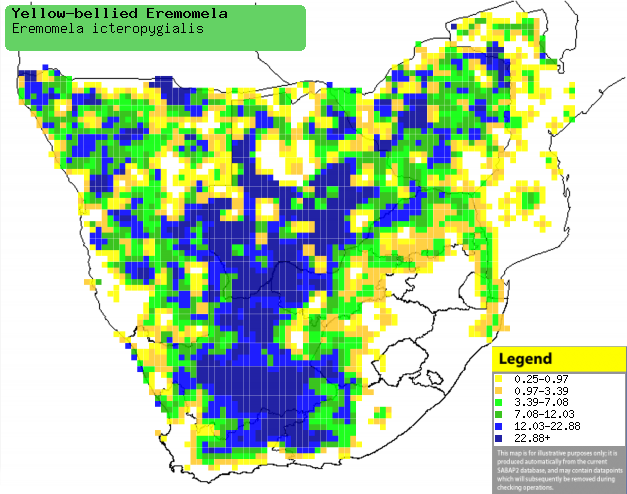
Distribution of Yellow-bellied eremomela in
southern Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from
first SA Bird Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Klaas's cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats insects, supplemented with fruit, seeds and
nectar. It typically forages in the foliage of bushes and saplings, gleaning
food from leaves and twigs and sometimes joining mixed species foraging flocks. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Insects
- Fruit
- Seeds
- Aloe greatheadii (Spotted aloe) nectar
Breeding
- The nest is a tidy, thin-walled cup built of stringy plant fibres and dry
grass and secured with spider's web and plant down. It is typically placed
between lengthwise twigs on the edge of a bushes or sapling's foliage.
- Egg-laying season is from about August-January, peaking from
September-November.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated for 13-14 days, probably by both
sexes.
- The chicks are fed by both adults, leaving the nest after about 15-16
days, remaining under their parents for about 2 more weeks, sometimes more.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
-
Harrison, J.A., Allan, D.G., Underhill, L.G., Herremans, M.,
Tree. A.J., Parker, V. & Brown, C.J. (eds). 1997. The atlas of southern
African birds. Vol. 2: Passerines. BirdLife South Africa, Johannesburg.
|
