|
Cryptillas victorini
(Victorin's warbler)
[= Bradypterus victorini]
Rooiborsruigtesanger [Afrikaans]; Victorin-struikzanger
[Dutch]; Bouscarle de Victorin [French]; Rostbrust-buschsänger [German];
Felosa de Victorin [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sylviidae
 |
 |
|
Victorin's warbler, Harold Porter Botanical
Gardens, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Victorin's warbler, Harold Porter Botanical
Gardens, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to South Africa, occurring from the Cedarberg
mountains to Uitenhage, in the Eastern Cape. It generally prefers moist, rank
bush, such as mountain fynbos found along streams.
|
 |
|
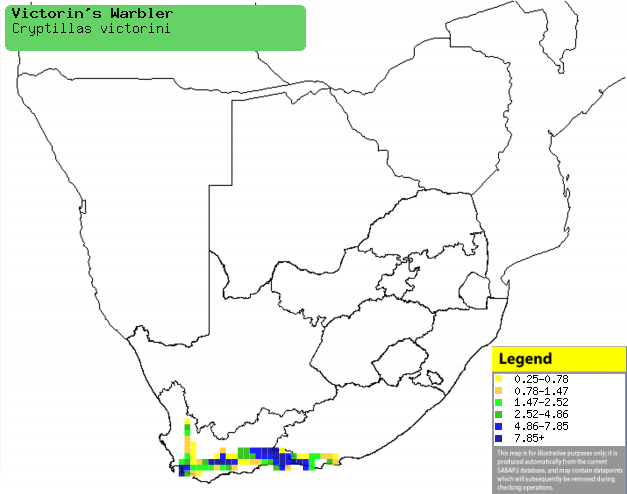
Distribution of Victorin's warbler in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Its feeding habits are little known, but it has been
observed foraging on the ground, catching beetles mantids and grasshoppers.
Breeding
- Only 3 nests have been found in southern Africa, and interestingly they
vary in their descriptions. They all were bowl-shaped, but one was made of
dead banana sheathing, the other was built of strips of millet bound with
spider web, and the other was made of grass, twigs and leaves. They were
lined with soft material and placed in the center of grass tussocks.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated mainly by the female.
- No information is available about the chicks, other than that they are
fed by both parents.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
