|
Tringa ochropus (Green
sandpiper)
Witgatruiter [Afrikaans]; Witgatje [Dutch]; Chevalier
cul-blanc [French]; Waldwasserläufer [German]; Maçarico-bique-bique
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Charadriiformes > Family: Scolopacidae
Distribution and habitat
Breeds in a broad belt of forest and taiga from 50-65°
North, heading south in the non-breeding season to the Mediterranean, southern
Asia and sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal to Ethiopia south to southern Africa.
Here it is generally scarce, occurring in patches of Zimbabwe, Limpopo Province,
northern and southern Botswana and central Mozambique, generally preferring
small streams, pools in vleis and woodland, ditches and moist margins of large
water bodies.
|
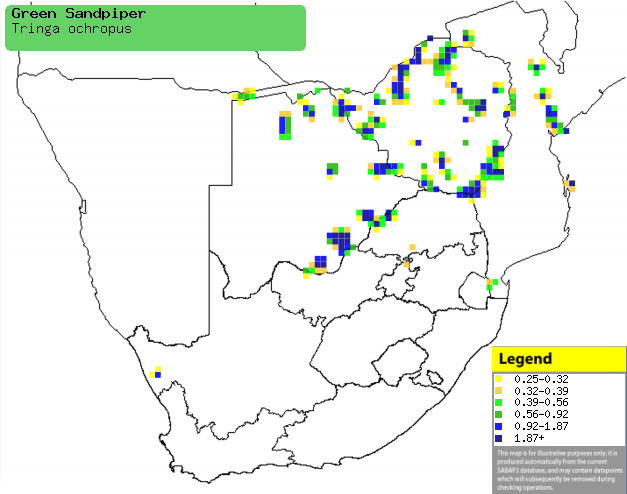 |
|
Distribution of Green sandpiper in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Non-breeding migrant to southern Africa,
arriving in early September and August and leaving in the period
from April-May.
Food
It mainly eats insects, crustaceans, spiders, molluscs,
annelids, fish and plant material, doing most of its foraging under overhanging
vegetation, plucking prey from the ground or shallow water or trembling its foot
in water to disturb resting animals.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
