|
Crecopsis egregia (African crake)
[= Crex egregia]
Afrikaanse riethaan [Afrikaans]; Katukutuku (generic term for
crake) [Kwangali]; Nhapata (generic name for coot, gallinule, moorhen,
crake or rail) [Shona]; Râle des prés [French]; Steppenralle [German];
Codornizão-africano [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Gruiformes > Family: Rallidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across sub-Saharan Africa; in southern Africa it is locally common in
Zimbabwe, northern and eastern Botswana, north-eastern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip), north-eastern South Africa and central and southern Mozambique.
It generally prefers dry grassland in savanna, also moving into rice, sugar
cane, maize and cotton fields, abandoned agricultural land and airfields.
|
 |
|
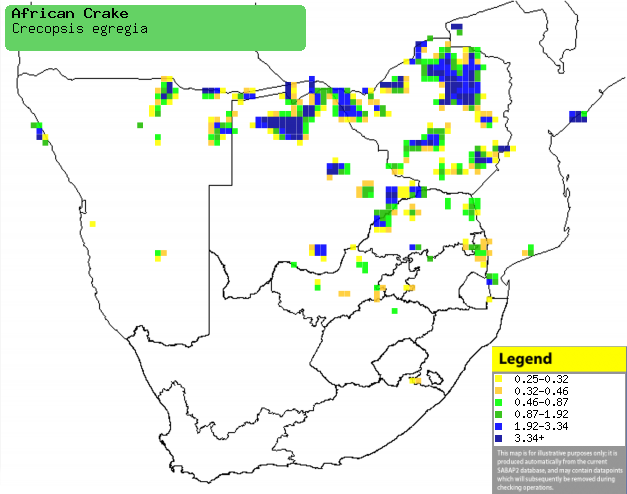
Distribution of African crake in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
- Predators
- of adults
- of chicks
- Dispholidus typus (Boomslang)
Movements and migrations
Intra-African breeding migrant, breeding in
southern Africa from October-April before heading north to its
non-breeding grounds in equatorial Africa, mainly travelling at
night.
Food
Mainly eats insects, earthworms, small frogs, plant matter
and fish, doing most of its foraging beneath vegetation or along roads, turning
over leaf litter and dead grass and probing the soil and grass tufts in search of
prey. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Animals
- invertebrates
- vertebrates
- Plant matter
- seeds
- grass leaves
- green shoots
Breeding
- Monogamous solitary nester, vigorously defending its territory by
attacking intruders with its beak and regularly calling and displaying.
- The nest (see image below) is a saucer-shaped pad of dry grass,
typically placed in a grass or sedge tuft, especially if it is on wet
ground.
 |
|
|
African crake at its nest, Nylsvley area, South
Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from October-March, peaking from January-February.
- It lays 2-8, usually 5-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for
approximately 14-24 days.
- The chicks leave the nest soon after hatching and cared for by either
one or both parents.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
