|
Agapornis roseicollis (Rosy-faced
lovebird)
Rooiwangparkiet [Afrikaans]; Perzikkopagapornis [Dutch];
Inséparable rosegorge [French]; Rosenpapagei [German];
Inseparável-de-faces-rosadas [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Psittaciformes > Family: Psittacidae
The Rosy-faced lovebird is found exclusively in Namibia, but
it is a popular cage bird worldwide, so escapees can be found outside its wild
range. It lives in various types of woodland, often with rivers
nearby. It eats mainly seeds, the rest being largely made of fruits and, rarely,
flowers. It lives in noisy gregarious colonies, which use many different types of
nesting sites. It lays 4-6 eggs, which are incubated by the female only, for 23
days. The female broods and feeds the chicks, while the male does all the
foraging.
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to Namibia, marginally extending into the
Northern Cape, south-western Botswana and southern Angola. It is a common house
pet, so escapees may crop up anywhere in southern Africa and the rest of the
world. In the wild it generally prefers mature woodland along ephemeral rivers,
especially stands of Northern lala palms
(Hyphaene petersiana) or a mix of Acacia,
star-chestnuts (Sterculia) and corkwoods (Commiphora).
|
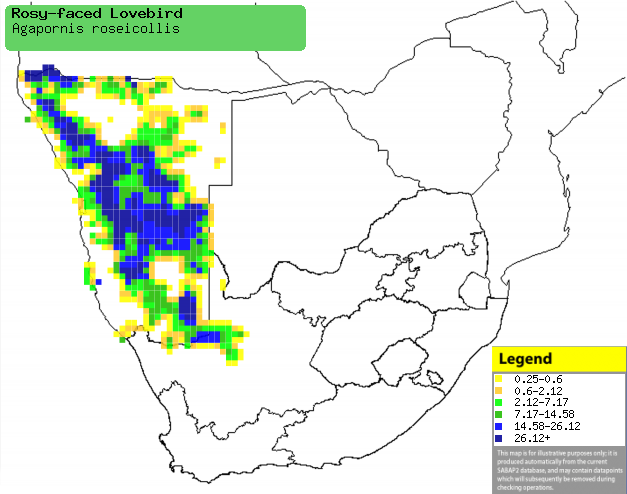 |
|
Distribution of Rosy-throated lovebird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Mainly eats seeds, often
foraging on cultivated land. The following plant products have been recorded in its diet:
- Plants
- seeds
- Pennisetum mezianum
- Achyranthes (burweed)
-
Acacia
- sunflower
- millet
- maize
- fruits
- Rhus (Currants)
- Commiphora (Corkwoods)
- Ficus sur (Broom-cluster fig)
- Albizia
- flowers
- leaves
Breeding
- Gregarious and noisy colonial nester, typically nesting in rock crevices, holes in buildings
and communal nests of
Philetairus socius
(Sociable weaver). The interior is often lined with bark strips and grass
leaves.
- It lays its eggs from February-April, peaking from February-March.
- It lays 4-6 eggs (3-8 in captivity) at 2 day intervals.
- Incubation starts 1-2 days after the first laid egg, and is done solely by
the female for about 23 days.
- The newborn chicks are reddish, becoming grey as they grow older. They are
brooded by the female, while the male does all the foraging.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
