|
Cyanomitra veroxii (Grey
sunbird, Mouse-coloured sunbird)
[= Nectarinia veroxii]
Gryssuikerbekkie [Afrikaans]; Grijze honingzuiger [Dutch];
Souimanga murin [French]; Graunektarvogel [German]; Beija-flor-cinzento
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Nectariniidae
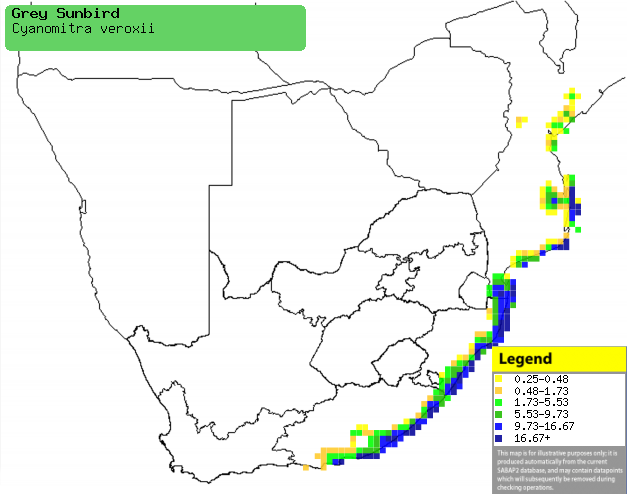
Distribution and habitat
Occurs along the eastern coastline of sub-Saharan Africa,
from Somalia through Kenya and Tanzania to southern Africa. Here it is locally
common down the coast from eastern Mozambique to KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern
Cape, generally preferring coastal evergreen forest, well-developed valley
bushveld and patches of Afromontane forest further inland.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Grey sunbird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Klaas's cuckoo.
Movements and migrations
Nomadic and partially migratory, as it is
thought that it migrates from the Eastern Cape to KwaZulu-Natal in
Winter.
Food
It mainly eats nectar, foraging throughout the day and also
eating termites and other small arthropods. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Nectar
- Schotia brachypetala (Weeping boer-bean)
- Schotia afra (Karoo boer-bean)
- Erythrina caffra (Coastal coral-tree)
- Tecoma capensis (Cape honeysuckle)
- Aloe arborescens (Krantz aloe)
- Strelitzia
- Arthropods
Breeding
- The nest is a peculiar oval-shaped structure with a side entrance covered
by a large flap, often with a long tail of material protruding from its
base. It is usually built of fine, hair-like fibres such as Marasmius
fungus, camouflaged with a thick layer of dead leaves and leaf petioles and
lined with dry grass. It is typically suspended at the roof by a long strand
of material to a twig or creeper overlooking a small forest clearing, path
or road, or occasionally from roots on the side of an erosion gullly and
even in little-used buildings.
- It lays 1-4, usually 2-3 chocolate brown eggs, usually in the period
from September-January.
Threats
Not threatened, although extensive destruction of forests
in southern Mozambique and KwaZulu-Natal is definitely cause for concern.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
