|
Oenanthe bifasciata (Buff-streaked chat)
Bergklipwagter [Afrikaans]; Inkotyeni, Isixaxabesha (these terms also
applied to Capped wheatear) [Xhosa]; iNkolotsheni [Zulu]; Tantabe [North
Sotho]; Streeptapuit [Dutch]; Tarier bifasciť [French];
Fahlschulterschmštzer [German]; Chasco-estriado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Muscicapidae > Genus: Oenanthe
 |
 |
|
Buff-streaked chat male, with caught insect in its
bill. [photo Johann Grobbelaar ©] |
Buff-streaked chat female, with caught insect in
its bill. [photo Johann Grobbelaar ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to of South Africa, Swaziland and Lesotho,
occurring along much of the Drakensberg escarpment and surrounding foothills. It
generally prefers grassland on boulder-strewn slopes or rocky outcrops, with
scattered bushes and trees. It may also occur around farmhouses and at the edges
of human settlements, where it often becomes tame.
|
 |
|
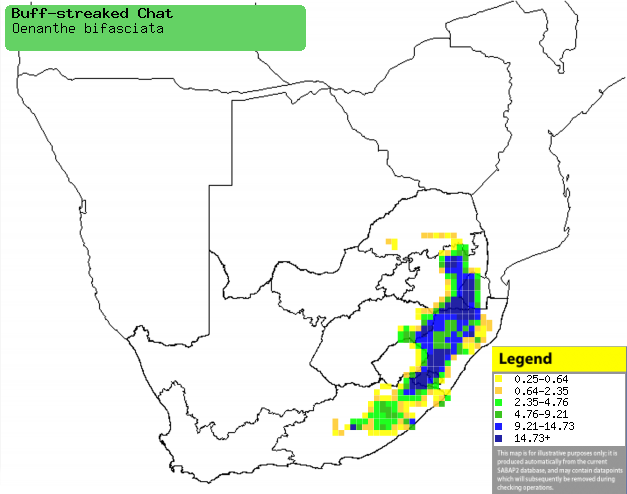
Distribution of Buff-streaked chat in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats arthropods, doing most of its foraging from
a perch on a boulder (see images above), from which it pounces on prey on the
ground and in the air. It also forages on the ground, and it may even glean food
from the leaves and branches of trees. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Seeds
- Nectar of Aloe vryheidensis (Vryheid aloe)
Breeding
- The nest is mainly built by the female and is a cup set into a large,
untidy platform of grass and roots, lined with rootlets, hair and fine
grass.
- Egg-laying season is from September-February, peaking from
October-November.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female in shifts of
about half an hour, with roughly 15 minute breaks between them.
- The chicks are fed by both parents on a diet of grasshoppers,
caterpillars and other insects.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
