|
Monticola angolensis (Miombo rock-thrush)
Angolakliplyster [Afrikaans]; Mugendasikarapi (generic term for thrush)
[Kwangali]; Miombo-rotslijster [Dutch]; Monticole angolais [French];
Miomborötel [German]; Melro-das-rochas-do-miombo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Muscicapidae > Genus: Monticola
Distribution and habitat
Occurs throughout south-Central Africa, from Tanzania
through southern DRC, Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa. Here it is locally
common in open miombo (Brachystegia) and Zambezi teak (Baikiaea
plurijuga) woodland, occasionally moving into Mopane (Colosphermum mopane)
and Uapaca kirkiana (Mohobohobo) woodland types.
|
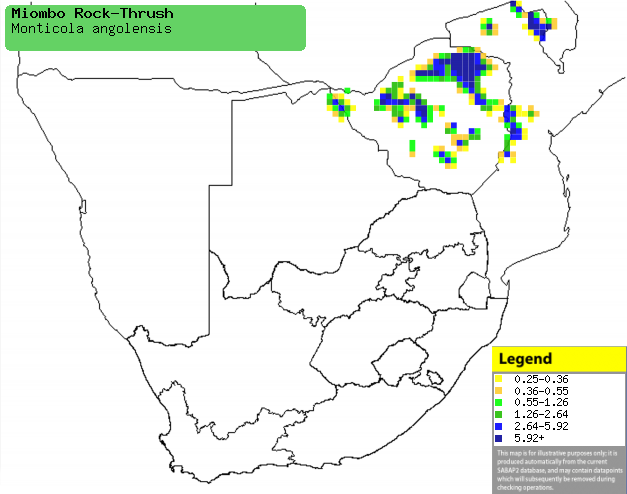 |
|
Distribution of Miombo rock-thrush in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Food
It mainly eats arthropods, doing most of its foraging in
the leaf-litter, gleaning prey from logs and bark. The following food items have
been recorded in its diet:
- Insects
-
Spiders
- False wireworm
- Typhlops (blind snake)
Breeding
- The nest is has a dense foundation of coarse grass and miombo (Brachystegia)
leaf petioles in which a cup-shaped cavity is positioned, lined with grass
and rootlets. It is typically placed in a shallow cavity in the main stem of
a tree, usually less than 2 metres above ground.
- Egg-laying season is from August-December, peaking from
September-November.
- It lays 3-4 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 13-15
days.
- The chicks are brooded solely by the female but fed by both parents,
leaving the nest after about 16-20 days. They eventually become independent
3-6 months after fledging.
Threats
Not threatened, although the clearance and fragmentation of
miombo (Brachystegia) woodland in Zimbabwe is definitely cause for
concern.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts - Birds of
southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book
Fund, Cape Town.
|
