|
Trochocercus cyanomelas
(Blue-mantled crested-flycatcher, Blue-mantled flycatcher)
BloukuifvlieŽvanger [Afrikaans]; Igotyi [Xhosa]; Kaapse
kuifmonarch [Dutch]; Tchitrec du Cap [French]; Blaumantel-schopfschnšpper
[German]; Papa-moscas-de-poupa [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Monarchidae
 |
|
Blue-mantled crested-flycatcher, Pietermaritzburg,
South Africa. [photo
Alan Manson
©] |
For information about this species, see
www.birdforum.net/opus/African_Crested_Flycatcher
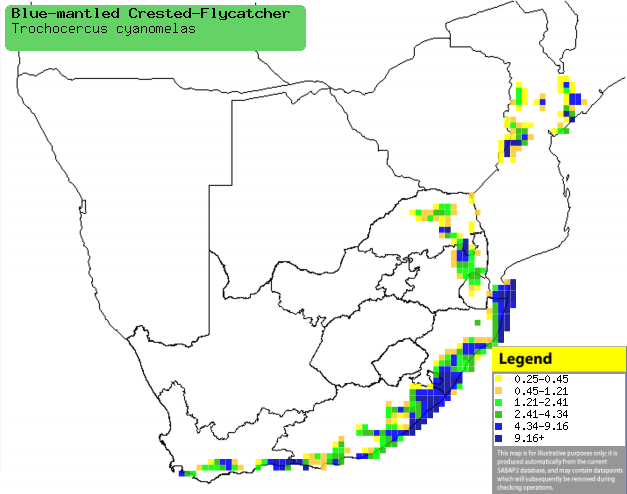
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to sub-Saharan Africa, it occurs from Somalia to
Kenya, through Tanzania to southern Africa. In this region, the bulk of its
population is in South Africa, in the Limpopo Province and coastal areas of
KwaZulu-Natal, Eastern and Wesern Cape, but it also has small popluations in
north-central Mozambique. It usually occurs in the undergrowth of thick
Afromontane, Evergreen and riverine forest, occasionally moving into thickly
wooded areas of valley bushveld.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Blue-mantled crested-flycatcher in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Its diet is exclusively made up of small invertebrates,
often foraging from a perch from which it takes short looping flights to hawk
prey items.
Breeding
- The nest is well-built thick-walled cup, made of bark fibres, moss, fine
grass and lichen, bound together withh spider web.
- Egg-laying season is from October-January, peaking from
September-December.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes each taking a circa
45 minute long shift.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
