|
Pogoniulus bilineatus
(Yellow-rumped tinkerbird, Golden-rumped tinker barbet)
Swartblestinker [Afrikaans]; Geelstuit-ketellapper
[Dutch]; Barbion à croupion jaune [French]; Goldbürzel-bartvogel [German];
Barbadinho-de-rabadilha-limão [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Piciformes >
Family: Lybiidae
The Yellow-rumped tinkerbird occurs from Senegal east
through the Sahel to Uganda, extending south to Angola and the eastern
coast of southern Africa. It mainly eats fruit, with the remainder of its diet
insects and nectar, foraging in the upper canopy of trees. Both sexes excavate
the nest, which is a chamber in the underside of a dead branch. It lays 2-4
eggs, which are incubated by both sexes.
Distribution and habitat
Its distribution is centred on West Africa and the DRC, extending south to
northern Angola, northern Zambia and the eastern
coast of southern Africa. It generally prefers evergreen and moist
lowland forest.
|
 |
|
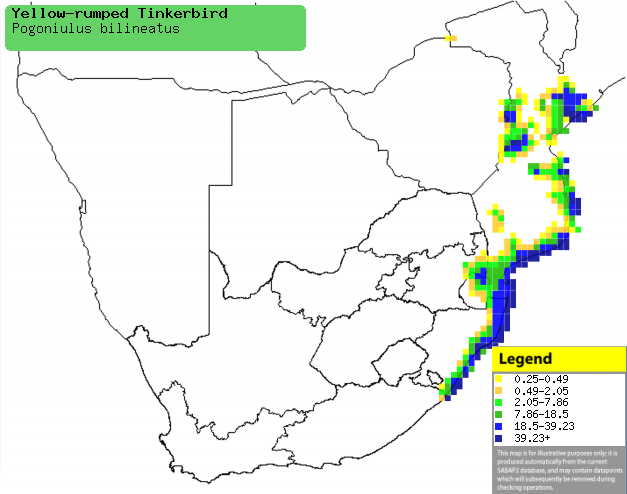
Distribution of Yellow-rumped tinkerbird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Scaly-throated honeyguide.
Food
It mainly eats fruit, supplemented with insects and nectar, foraging in the upper
tree canopy.
The following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Plants
- fruit
- mistletoes
- Tapinanthus
- Erianthemum
- Helixanthera
- Viscum
- Ficus (wild figs)
- Trema orientalis (Pigeonwood)
- Apodytes dimidiata (White-pear)
- Bridelia micrantha (Mitzeerie)
- Antidesma venosum (Tasel-berry)
- Allophylus natalensis (Dune false-currant)
- Scutia myrtina (Cat-thorn)
- Grewia flavescens (Sandpaper raisin)
- Stelitzia nicolai (Coastal sterlitzia)
- nectar of
Aloe marlothii (Mountain
Aloe)
- Insects
Breeding
- Both sexes excavate the nest, which is a
chamber in the underside of a dead branch.
- Egg-laying season is from July-February in Zimbabwe and from
October-March in South Africa.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes.
- Little is known about the development and care of the chicks.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
