|
Sterna paradisaea (Arctic tern)
Arktiese sterretjie [Afrikaans]; Unothenteza (also applied
to Common tern) [Xhosa]; Noordse stern [Dutch]; Sterne arctique [French];
Küstenseeschwalbe [German]; Gaivina-árctica [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Charadriiformes
> Family: Laridae > Genus: Sterna
 |
|
|
Arctic tern in non-breeding plumage, Pelagic trip
off of Cape Town, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
Breeds from North America to the White Sea of Russia,
heading south in the non-breeding season to the Southern Ocean and adjacent cold
sea in the Humboldt Current passing South America and the Benguela Current passing southern Africa.
Within southern Africa it is uncommon off the west coast, while more scarce
further out to sea and off the southern and eastern coast of the region.
|
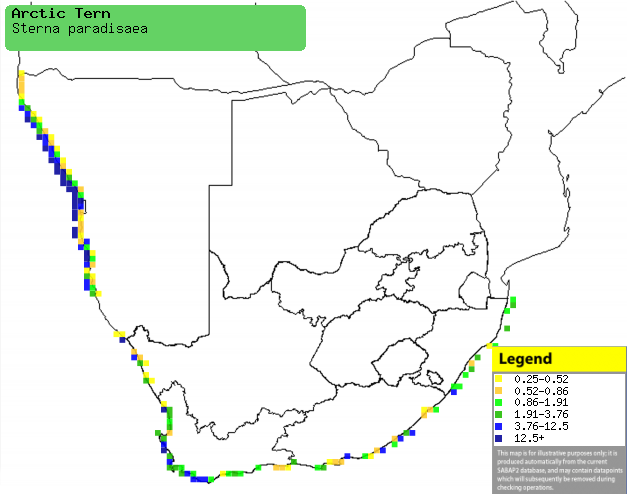 |
|
Distribution of Arctic tern in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Migratory, with some performing of the longest
migrations of any bird; it is mainly passage migrant through
southern African waters, occurring from September-January.
Food
Mainly eats small fish, doing most of its foraging by
rapidly flying over the sea, hovering once it spots prey before plunge-diving
into the water.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
