|
Columba guinea (Speckled
pigeon, Rock pigeon)
Bosduif [Afrikaans]; Kransduif
[Afrikaans]; Ivukuthu [Xhosa]; iJuba (also applied to Eastern bronze-naped
pigeon), iVukuthu [Zulu]; Haifoko [Kwangali]; Leeba (generic term for pigeon or
dove), Lehoboi, Leeba-la-thaba [South Sotho]; Leeba (generic term for pigeon or
dove), Leebarope, Letseba [Tswana]; Gespikkelde duif [Dutch]; Pigeon roussard
[French]; Guineataube [German]; Pombo-malhado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Columbiformes > Family:
Columbidae > Genus: Columba
 |
 |
|
Speckled pigeon, West Coast Fossil Park, Western Cape, South Africa. [photo H. Robertson,
Iziko ©] |
Speckled pigeon, Kleinmond, Western Cape, South Africa. [photo
Duncan Robertson
©] |
The Speckled pigeon is common in many places in southern
Africa, especially in South Africa. It usually lives in rocky, mountainous
areas, but can also be found in buildings and gardens. It feeds mostly on seeds,
rarely eating small fruits and flowers. The nest is usually placed on ledges,
gullies or buildings, and is built by the female, with the male collecting the
material. It lays 1-3 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes. The chicks are
brooded for the first 6 days of their lives, after which brooding ceases. The
nestling period is highly variable with different regions, full range 21-37
days.
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Senegal to Ethiopia south to Tanzania, with a
separate population in south-western Angola and southern Africa. With in
southern Africa it is common in western and central Namibia, southern Botswana,
Zimbabwe (marginally extending into Mozambique), Swaziland, Lesotho and South
Africa. It generally prefers rocky
areas with mountains, cliffs and gorges, but it has recently taken to urban and
rural buildings, where it often roosts and nests.
|
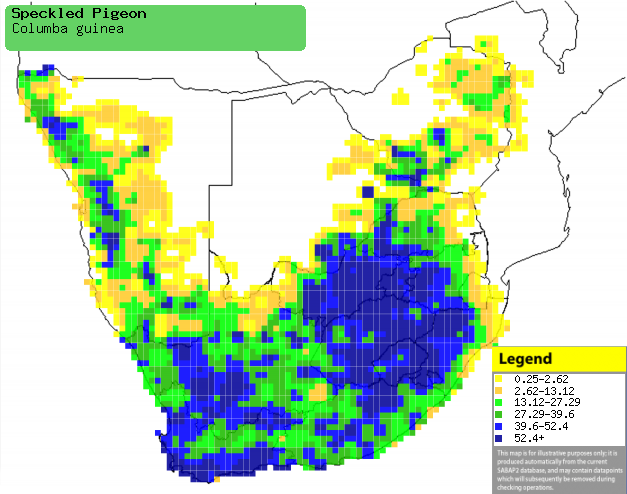 |
|
Distribution of Speckled pigeon in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
Food
Feeds mainly on seeds, rarely eating
fruits and leaves. It typically forages on the ground, usually on farmland, lawns or roads. The
following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Plants
- seeds
- grasses
- Jagopyrum esculentum (Wild buckwheat)
- Tribulus terrestris (Devil thorn)
- Amaranthus (Pigweeds)
- crops
- sunflowers
- wheat
- sorghum
- maize
- groundnuts
- Arctotheca nivea (Sea-pumpkin)
- fruits
- Jatropha zeyheri (Spurge)
- Ficus (Wild figs
- flowers
- Cynodon dactylon (Lawn grass)
- Poa annua (Lawn grass)
- leaves of Silene bellidoides (Wild tobacco)
- acorns of Quercus robur (European oak)
Breeding
- It makes its own nest, with the male collecting material
and giving it to the female, who then puts it into the nest. This consists
of a collection of twigs, grass, herbs and sometimes wire, shotgun shells and
nails, usually placed on ledges of cliffs, in caves, gullies or often in
buildings.
- It lays 1-3 eggs, at any time of year.
- Incubation is done by both parents for about 14-16 days, changing shifts at
mid-morning and late afternoon.
- The chicks are brooded for the first six days of their lives, after which
brooding ceases. The nestling period is highly variable with different
regions, ranging from 21-37 days.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact quite common across southern
Africa. It has adapted very well to living with humans, as it often nests and
roosts in buildings.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
