|
Alcedo cristata (Malachite
kingfisher)
Kuifkopvisvanger [Afrikaans]; Isaxwila (generic term for
kingfisher) [Xhosa]; iNhlunuyamanzi, isiKhilothi, uZangozolo (also applied to
African pygmy-kingfisher) [Zulu]; Seinoli (generic term for kingfisher) [South
Sotho]; Chinderera, Kanyururahove [Shona]; Sipholoti (also applied to
Brown-hooded kingfisher) [Swazi]; Tshololwana (generic term for kingfisher)
[Tsonga]; Mmatlhapi, Seinôdi (generic terms for kingfisher) [Tswana];
Malachietijsvogel [Dutch]; Martin-pêcheur huppé [French]; Malachiteisvogel,
Haubenzwergfischer [German]; Pica-peixe-de-poupa [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Coraciiformes >
Family: Alcedinidae
 |
 |
| Malachite kingfisher.
[photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Malachite kingfisher juvenile.
[photo Callie de Wet ©] |
 |
 |
| Malachite kingfisher, with caught
tadpole in its beak, Paarl Bird Sanctuary, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Malachite kingfisher taking off, Paarl Bird
Sanctuary, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
The Malachite kingfisher is common in many areas of southern
Africa, living in a wide variety of aquatic habitats. It feeds mainly on fish,
as well as amphibians and insects. Both sexes dig a burrow, which is used as a
nesting site, and placed in the banks of rivers or streams. It lays 3-6 eggs,
which are incubated by both sexes, for 14-16 days. The chicks are brooded for
the first few weeks of their lives, before leaving the nest at 22-25 days old.
They start fishing within one week of fledging, sometimes "catching" twigs and
leaves. They are chased away by their parents at 36-41 days old.
Distribution and habitat
Common across much of sub-Saharan Africa; within southern
Africa it occurs in northern and southern Namibia, northern and south-eastern
Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and South Africa. It occupies a variety of
aquatic habitats, including
slow-moving rivers and streams, dams, sheltered shores, coastal lagoons, tidal
estuaries, mangrove swamps, sewage ponds, irrigation canals, mangroves, reed or
papyrus marshes, seasonal streams and temporary ponds. It normally breeds in small
watercourses, with steep banks for nesting holes and plenty of thickets and
reeds.
|
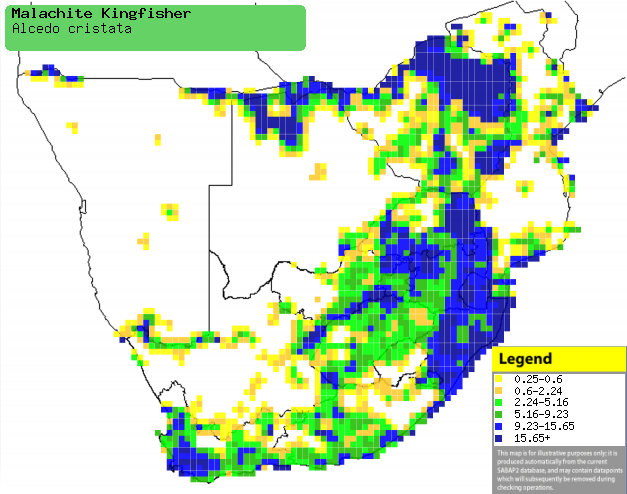 |
|
Distribution of Malachite kingfisher in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Its diet varies greatly in
different regions, although its diet is usually dominated by fish, as well as frogs,
tadpoles and aquatic insects. It hunts by sitting on a perch, staring intently
into the water in search of prey. Once prey is located, it dives steeply in the
water, grabbing with its bill. The following food items have been recorded in
its diet:
- Vertebrates
- small fish
- Oreochromis alcalicus (Tilapia)
- Aplocheilichthys johnstoni (Johnston's topminnow)
- amphibians
- frogs
- tadpoles (see bottom left image)
- reptiles
- Invertebrates
- insects
- Oligochaete worms
- small crustaceans
Breeding
- Both sexes participate in excavating a burrow nest, which is dug into the earthen bank
of a stream or river. It consists of a
tunnel going 0.25-1.2m into the ground, ending in a 9cm wide nest cavity.
Interestingly, it constructs 2-3 burrows simultaneously, but only completing
one.
- It usually lays it's eggs when the water level is low, but there are
exceptions. Laying dates are as follows:
| |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
| Botswana |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Zimbabwe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mozambique |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| North-eastern South Africa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Western Cape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
It lays 3-6 eggs at one day intervals, which are
incubated by both sexes for 14-16 days.
-
The chicks are fed mainly fed Tilapia (Oreochromis alcalicus), and at
one point weigh more than their parents. The
amount of food they are given decreases as their fledging period grows
nearer, leading to the nestlings losing weight.
-
The chicks are brooded mainly by the female, until
their eyes open at 10-12 days old. They leave the nest at 22-25 days
old, fledging one or two days later. They start fishing within one week
of fledging, sometimes catching twigs and leaves instead of prey. They
are chased away by their parents at 36-41 days old.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact common in many areas of southern
Africa.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
